Numerical Simulations of a Nonlocal Delayed Reaction-Diffusion Model
To illustrate the formation and stability of wave solutions we turn our attention to a class of nonlocal delayed RD equation proposed by So et al (2001, Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A, 457, 1841–1853). In particular, the authors adopted Smith-Thieme’s approach to obtain the following model of single species population.
\( \frac{\partial w}{\partial t} = D_m\,\frac{\partial^2 w}{\partial x^2} - d_m w + \varepsilon \int_{-\infty}^{\infty} b\!\big(w(y,t-\tau)\big)\, f_{\alpha}(x-y)\,dy, \)
The kernel function is given by \(f_{\alpha}(x) = \frac{1}{\sqrt{4\pi\alpha}}\, e^{-x^{2}/(4\alpha)} \quad \text{with} \quad \alpha = \tau D_I > 0,\ \tau > 0.\)
We study
1. Convergence of PDE solution to wavefronts
2. Impacts of the diffusion rates on wave solutions
1. Convergence of PDE solution to wavefronts
Convergence to Stationary Wavefront
It is numerically shown that the solution of the initial value problem corresponding to the model may converge to the stationary wave front of the model.
blue= PDE Solution
red = Stationary Wavefront
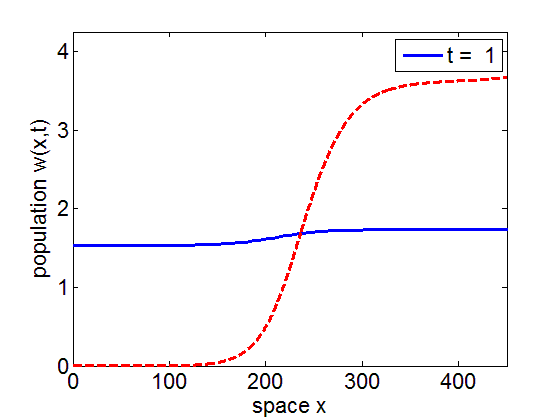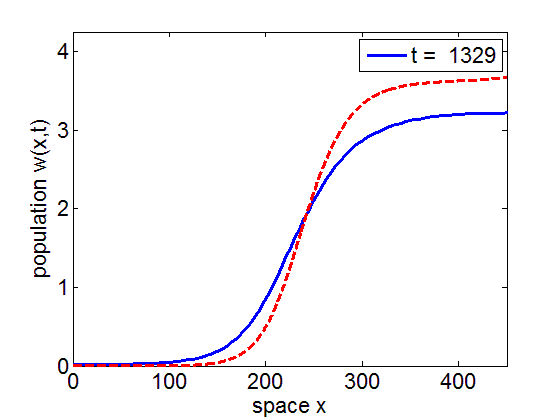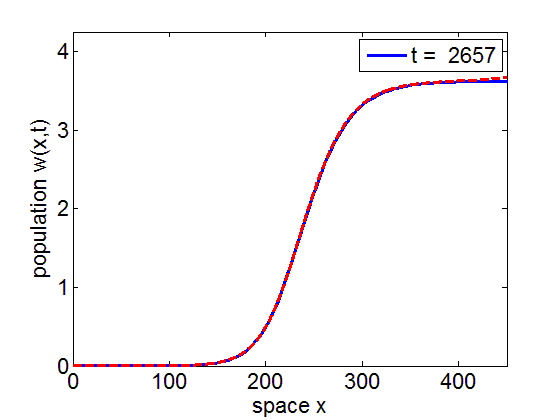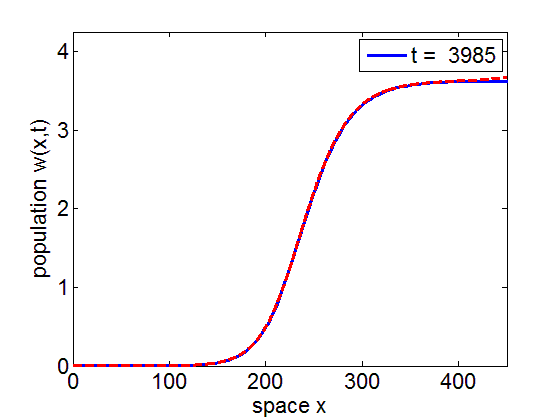
Convergence to Stationary Wave Pulse
It can be numerically shown that the solution of the initial value problem corresponding to the model may remain in a neighborhood of the stationary pulse and fronts of the reduced model for long periods of time.
blue= PDE Solution
red = Stationary Wave Pulse
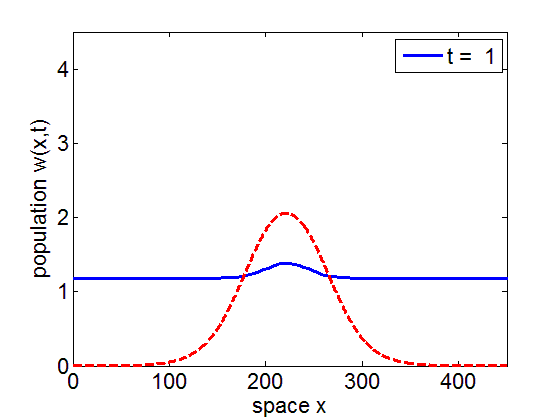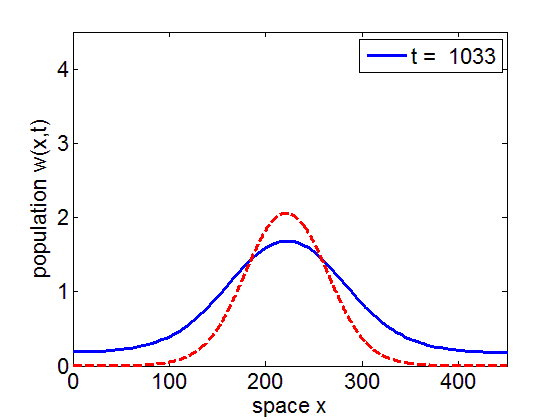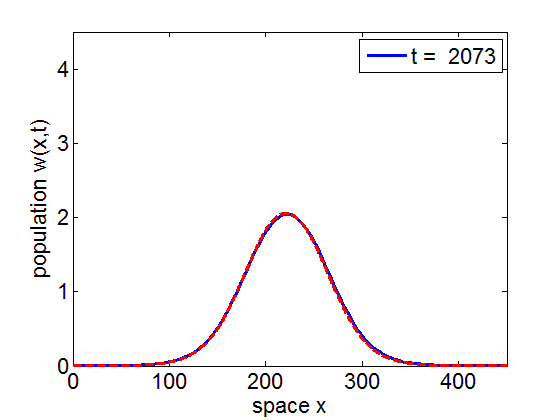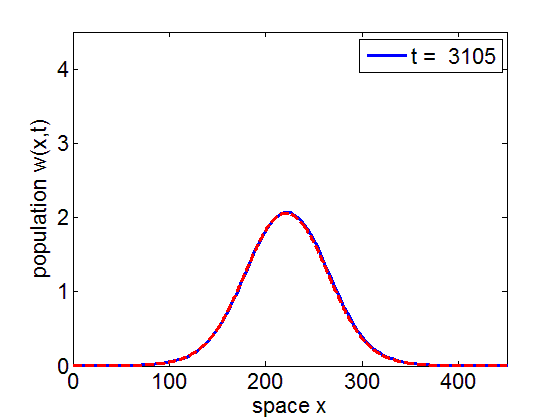
Formation and disappearance of a wave pulse in the 2-dimensional domain for the reduced model
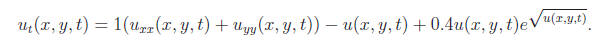
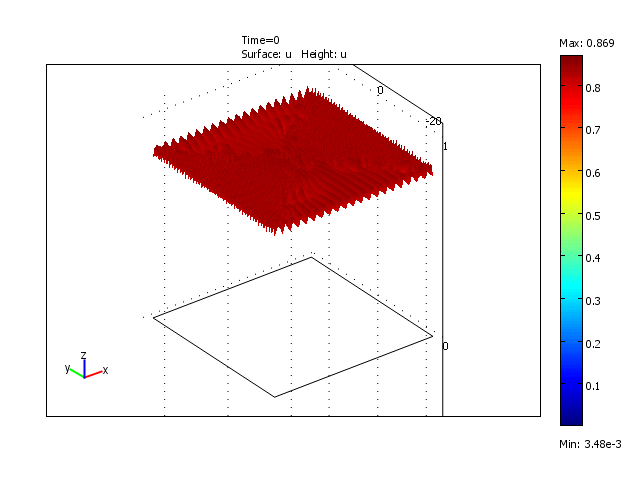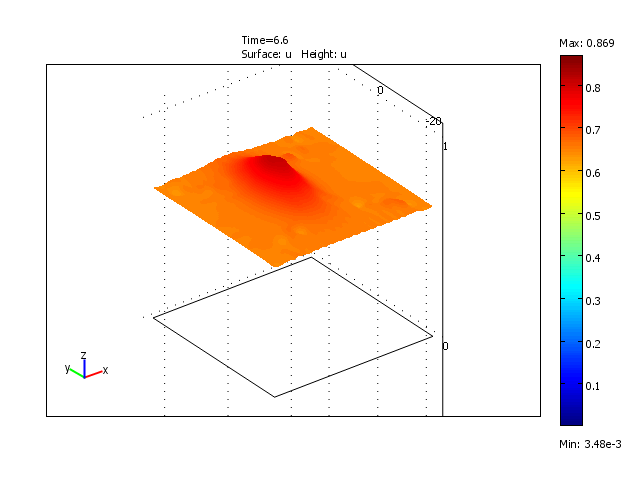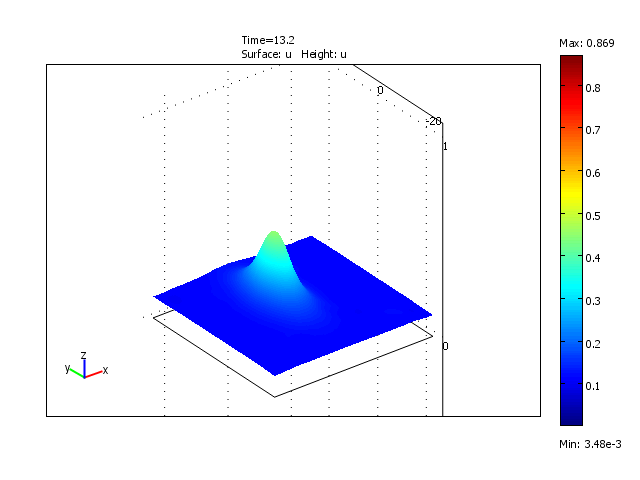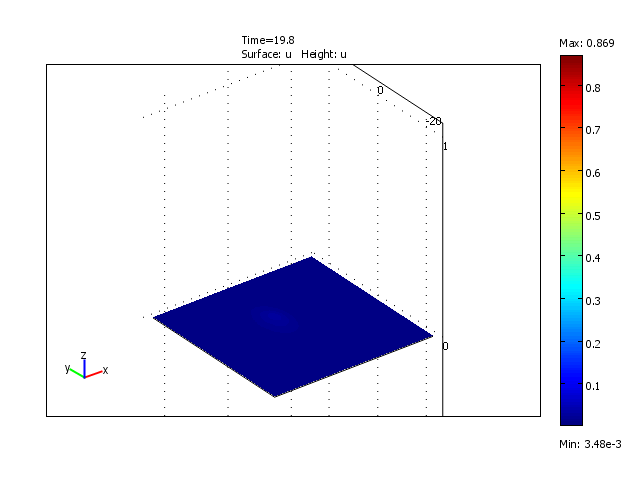
Formation of the traveling waves of the model with constant delay (τ = 12)

Formation of traveling waves with Gibbs phenomenon due to increasing delay

PDE solution for τ = 11

Formation of a wavefront in a 2-dimensional domain for the reduced model


