Purpose: This study adopted a quantitative design to evaluate a new latent construct, “Parental Academic Commitment (PAC)”, that was composed of parental involvement (PARINVOL) and parents’ expectations of their children’s academic success (PAREXPT). Furthermore, we also explored how different perceptions of school leadership would impact parental academic commitment and student learning. More specifically, we compared how principal-perceived school leadership and teacher-perceived leadership would influence student achievement (SA) directly and indirectly through mediating parental academic commitment (PAC). Methods: To find answers, we utilized two Structural Equations Models—Multiple Indicators and Multiple Causes Analysis (SEM-MIMIC) to first confirm the psychometric properties of PAC, and then compared the two SEM models. Data from 202 principals, 4251 teachers, 10,291 parents, and 10,291 students in Hong Kong and Macao from PISA 2022 were utilized; both individual-level and school-level analyses were conducted. Results: Principal-rated and teacher-rated school leadership functioned differently in the 2 SEM models. Both ESCS (Economic, Social, and Cultural Status) and PAC were confirmed to be significant contributors to positive student outcomes.
Publications
2025
2024
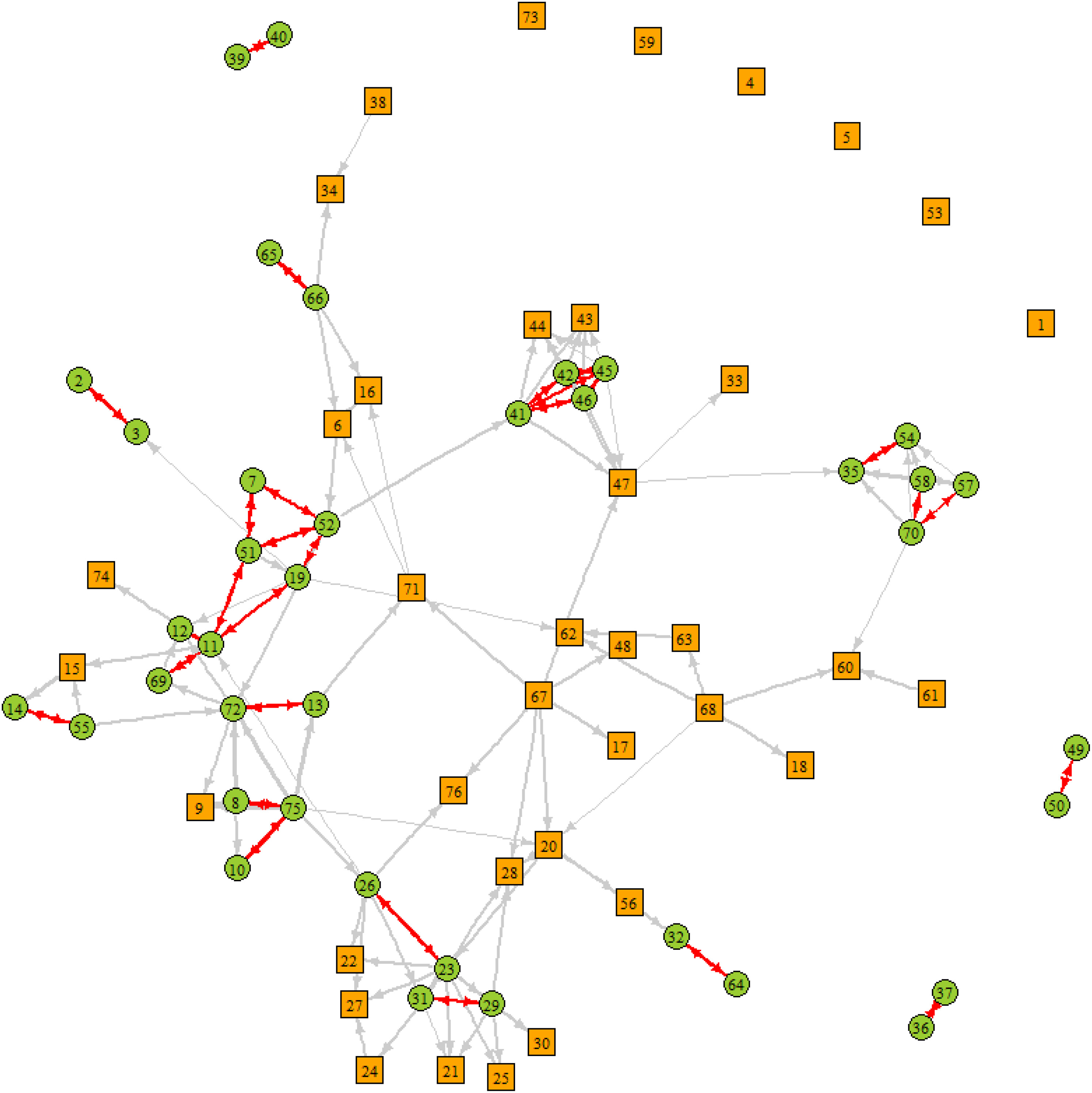
Various forms of networks in education have been proposed by scholars, policymakers, and educational administrators as a strategy for school improvement. However, there are few empirical studies on the effect of interschool networks. We analyzed data from 76 elementary schools in a Midwestern state to examine the association between interschool relationships and student achievement by employing social network analysis and hierarchical linear modeling (HLM). After controlling for school and district demographic characteristics, we found that (a) schools that reported to have a stronger relationship with other schools had better math achievement, and more growth in reading achievement; (b) schools with reciprocal relationships had better math and reading achievement, and more growth in reading achievement; and (c) schools that connected to more influential schools in the network had better math and reading achievement, and more growth in reading achievement. We discussed the implications for research, policy, and practice.
Principal leadership has been widely regarded as a powerful catalyst for school improvement and student learning. This article presents a multivariate meta-analysis of 42 empirical studies, published between 2000 and 2020, that examined the effects of principal leadership on student achievement in the United States. The focus is on the conceptual models and methodological approaches used to examine these effects. Our study reveals three major findings: (a) principal leadership had a positive impact on student achievement, when the effects were conceptualized as direct effects without controls (0.25 SD), or as indirect effects (0.22 SD); (b) the observed effects of principal leadership are contingent upon how impacts were conceptualized and analyzed; and (c) substantial heterogeneity existed in observed principal leadership effects, with student outcome measure serving as a significant moderator. We offer directions for future studies, including conducting more replication studies using high-quality approaches across different contexts; developing common typologies, sets of variables and their definitions and measurements; identifying significant mediators in the school process; applying multiple conceptual models and methodological approaches on a more comprehensive dataset; and moving beyond the effectiveness perspective to adopting an equity lens.
Michigan’s Great Start Readiness Program (GSRP) is a state-funded pre-K program that serves at risk four-year-old children across the state. Utilizing longitudinal data from 1,394 children in a mid-sized urban school district, we conducted regression analyses and piecewise linear growth models to examine the growth trajectory between GSRP children and non-GSRP children at each grade level from kindergarten to third grade in both reading and math. The results of regression analyses showed that, after accounting for other variables, participation in GSRP was statistically significantly associated with higher scores on Measure of Academic Progress (MAP) measures at various time points, ranging from 0.22-0.46 standard deviations (SD) in math and 0.31-0.49 SD in reading. The results of piecewise linear growth models illustrated that GSRP children had a statistically significantly faster monthly growth rate than non-GSRP children during the kindergarten year. However, the growth rates were not significantly different during the first, second, and third grade.
Despite the appeal of promoting and forming collaborative relationships between schools, empirical evidence for an association between school-to-school collaboration and school outcomes is still somewhat lacking. This study utilized data from 76 schools nested within 56 districts in the United States to examine the association between a school's reciprocal relationships and school outcomes by employing social network analysis and hierarchical linear modeling (HLM). After controlling for school and district demographic characteristics, we found the indices of reciprocal collaboration are associated with the school's 2018 student proficiency level in both math and reading and the growth in proficiency level between 2017 and 2018. The implications and limitations were discussed.
2023
Teacher leadership has been found to be positively associated with student achievement, and the dimensions of teacher leadership positively associated with teacher leadership have been identified. However, mechanisms to improve teacher leadership and the effects of these mechanisms are rarely studied. In this article, we report the efforts to develop teacher leadership in a multi-year, large-scale project titled, “HighImpact Leadership for School Renewal”, and the effects of these efforts. Repeated measure analysis was conducted to assess the project’s effect on teacher leadership using validated and published instruments. The results indicated that the project had large effects on enhancing teacher leadership, with Cohen’s d effect size ranging from 0.85 to 1.16 for scales of Orientation to School Renewal and from 0.87 to 1.13 for scales of Learning-Centered School Leadership. Implications for school renewal are discussed.
2022
A multivariate random-effects meta-meta-analysis was conducted to synthesize the association between principal leadership and student achievement. A total of 12 prior meta-analyses with 18 effect sizes were included in this meta-meta-analysis. The quantitative analysis showed that principal leadership has a statistically significant positive relationship with student achievement (Cohen's d = 0.34). The qualitative analyses revealed that: (a) with the accumulation of knowledge, there appears to have been a trend toward more consistent and precise estimates of principal leadership's effect on student achievement; (b) there was still not enough evidence to argue a specific leadership model or practice is more effective in improving student achievement than others; and (c) the educational contexts seem to moderate the effect of principal leadership. The significance and limitations of the current study, as well as the recommendations for future research, are discussed.
2021
Teacher leadership is commonly discussed in educational research and practice. Yet, the relationship between teacher leadership and student achievement has not been soundly established by empirical evidence. The purpose of this meta-analysis was to examine the extent to which teacher leadership was related to students’ academic achievement. The results revealed that teacher leadership was positively related to student achievement (r = .19). Among seven dimensions of teacher leadership which were all positively associated with student achievement, facilitating improvements in curriculum, instruction, and assessment has shown strongest relationship. The results of subgroup analysis indicated the relationships were similar among studies conceptualizing teacher leadership and using outcome measures differently, and for elementary and secondary school students. However, published studies reported larger effect sizes than unpublished studies. The implications and limitations are discussed.
Using a multilevel multiset time-series model, the present study aimed to examine whether changes in teacher perceived principal leadership practices were associated with the change in school academic performance. Teacher perceived principal leadership practices tapped into various aspects of school process and principal leadership. School academic performance was measured as a school’s average in reading and mathematics at a certain grade level (Grades 5–8) in a certain calendar year (2013–2017). Change in teachers’ perceptions regarding principals’ efforts to improve parent involvement was identified as the single most important teacher perceived principal leadership practice for growth in both school reading and school mathematics performance across grade levels (moderate effect size of .481 in reading and small effect size of .254 in mathematics). Implications were discussed, including the hypothesis of “growth” factors in principal leadership practice.
For this paper, we developed and validated the Orientation to School Renewal instrument,a 21-item instrument, based on seven factors, which allows schools to measure their school renewal efforts. The research is based on Goodlad’s notion of school renewal. Through an extensive literature review and our work over an eight-year period engaged in discussions with over 110 principals and 300 teachers, we gradually developed dimensions of the construct of school renewal. We then obtained survey data from a sample of 1,195 teachers in 83 schools, and validated the instrument using confirmatory factor analysis and other procedures. The seven factors identified from the literature and discussions with K-12 educators and confirmed via the validation process included: (a) focus on students and their achievements, (b) continuous school improvement, (c) balance between the internal and external influences, (d) the dialogue, decision, action and evaluation (DDAE) process, (e) implementation integrity, (f) implementers as active developers, and (g) internal responsibility and professionalism. Researchers and practitioners can use the instrument to collect valid and reliable data to measure, evaluate, and understand school renewal.
